What is a multi-armed bandit? Smarter experimentation for real-time marketing
Published on December 08, 2025/Last edited on December 08, 2025/9 min read


Team Braze
Marketers have long relied on A/B testing to refine campaigns, but that approach can leave insights sitting idle while opportunities pass by. The multi-armed bandit algorithm changes that. Instead of waiting until the end of a test to act, it continuously learns which variation—message, offer, or channel—performs best and adjusts traffic in real time.
This adaptive experimentation model helps brands make faster, smarter decisions using live performance data. Every impression contributes to optimization, allowing campaigns to evolve automatically rather than through manual tweaks. By blending testing and decisioning, the multi-armed bandit makes marketing feel more responsive and precise—giving customers what they want sooner, and giving marketers the confidence that each interaction is data-driven from the start.
Contents
Multi-armed bandit vs. traditional A/B testing
How marketers can use multi-armed bandits for optimization
Real-world applications: personalization, messaging, and offer testing
How Braze uses intelligent selection to bring MAB to life
Key takeaways: smarter experiments, faster wins
FAQs about the multi-armed bandit
What is a multi-armed bandit?
A multi-armed bandit is a type of testing algorithm that uses machine learning to automatically optimize campaigns in real time. It’s not a standalone tool or piece of software—it’s a decisioning approach built into platforms like Braze to help marketers make faster, smarter choices while a campaign is live.
Instead of splitting audiences evenly as in A/B testing, a multi-armed bandit continuously learns from engagement data and redistributes traffic toward the top-performing message, offer, or channel variation. This allows optimization to happen as results come in, not after the test ends.
The idea comes from probability theory and describes how to find the best option when several are available but their outcomes are unknown. In marketing, a single multi-armed bandit might test several subject lines for one email campaign, or a few variations of a push notification. The algorithm measures which version performs best in real time, automatically directing more traffic to it while still testing the others. With Braze, multiple bandits can run in parallel—each handling a different campaign, channel, or optimization goal.
Different mathematical models can power a multi-armed bandit. Two common ones are the Upper Confidence Bound (UCB) algorithm, which focuses on testing new options when performance differences are uncertain, and Thompson Sampling, which predicts the likelihood of success for each variation based on all results so far. Platforms that use multi-armed bandit testing, choose and run these models automatically. The marketer defines the goal, such as higher click rates or conversions, and the system continuously learns how to achieve it.
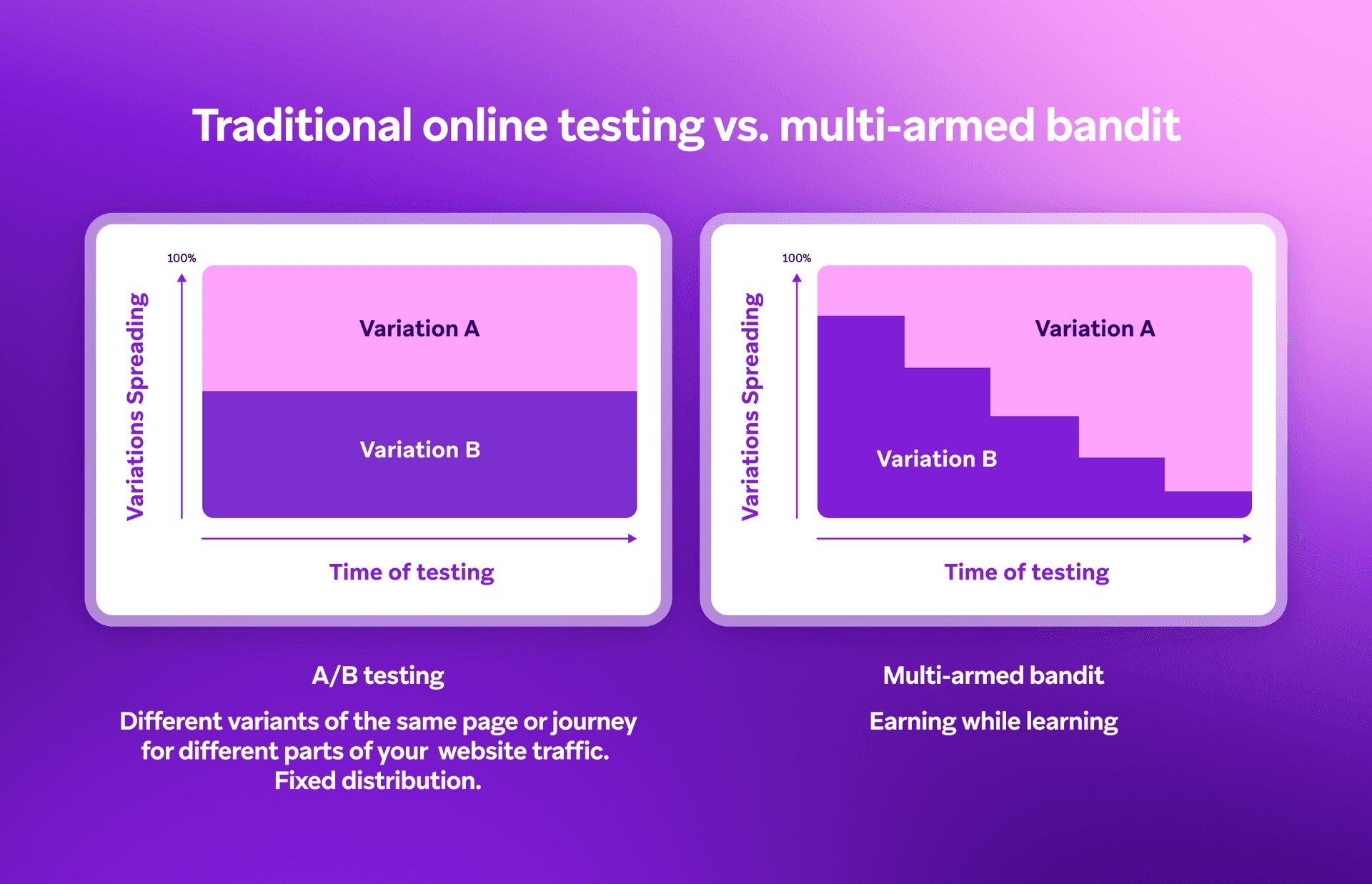
Multi-armed bandit testing vs. traditional A/B testing
A/B testing has long been the go-to method for comparing campaign variations. You create two or more versions, split your audience evenly, and wait until the test ends before acting on the results. It’s simple, reliable, and statistically clean—but it can be slow. While the test runs, most of your audience still receives the underperforming version, which can limit overall campaign results.
A multi-armed bandit starts learning as soon as the campaign launches. The algorithm monitors performance in real time and automatically shifts more traffic to the options that are performing best, while still exploring others to keep improving. This means more customers see stronger messages sooner, and the campaign keeps adapting without manual changes.
Where A/B testing is about validation, the multi-armed bandit is about adaptation. Both have a place in a marketer’s toolkit. A/B testing is best for setting overarching direction—like choosing between two homepage layouts or campaign concepts—while multi-armed bandit testing can then refine the individual elements within that framework, such as images, headlines, or button copy. That’s just one example, though. Bandit testing can be applied anywhere marketers want real-time learning—across offers, channels, or audience segments.
Used together, they form a complete experimentation framework: A/B testing helps you find direction, while multi-armed bandits help you stay responsive as that direction evolves.
How marketers can use multi-armed bandits for optimization
Multi-armed bandit testing gives marketers a way to keep improving campaigns without starting from scratch each time. Once a direction is set, the algorithm handles ongoing refinement—learning from each interaction and using that insight to improve future performance.
Marketers use this adaptive approach across many areas:
- Creative testing: Compare different subject lines, visuals, or CTAs to identify which combinations connect best.
- Offer strategy: Deliver the most relevant discount, bundle, or incentive to each audience segment based on live response data.
- Channel mix: Decide which touchpoint—email, push, or in-app—drives the strongest engagement for each user profile.
- Timing: Refine send windows dynamically so messages arrive when customers are most likely to engage.
Through dynamic optimization, every campaign becomes a live learning system—constantly evolving, aiming to reduce waste, and help improve results with each interaction. Here’s what that could look like:
Example use cases for multi-armed bandit testing
Industry: Retail and eCommerce
Goal: Identify the highest-converting “Add to Cart” button design on the product detail page.
Example use case: The brand tests several versions of the call-to-action button—different colors, copy (“Add to Bag,” “Shop Now,” “Get Yours”), and placements. The multi-armed bandit algorithm allocates more traffic to the versions that drive the most clicks and purchases while continuing to test underperforming ones in smaller volumes.
Outcome: The brand discovers the best-performing button combination in real time, boosting purchase intent without pausing traffic or delaying results.
Industry: Travel and hospitality
Goal: Increase click-through rates on personalized trip recommendation emails.
Example use case: The marketing team tests multiple subject lines, each highlighting a different type of travel—city breaks, beach escapes, or nature retreats. As the campaign runs, the bandit algorithm prioritizes the subject lines generating the most opens and clicks across user segments.
Outcome: The company improves engagement and booking rates by automatically serving the most appealing content themes to each traveler type.
Industry: Media and entertainment
Goal: Maximize engagement with push notifications promoting new content drops.
Example use case: The brand experiments with push notifications that vary in tone and timing—some highlight trending shows, others spotlight favorite genres. The bandit continuously analyzes open rates and view starts, redistributing impressions toward the most engaging messages.
Outcome: The platform increases watch-time and session starts while maintaining audience attention with timely, relevant notifications.
Industry: Financial services
Goal: Improve completion rates for online account applications.
Example use case: The company tests variations of its sign-up form layout and incentive messaging—different progress indicators, button copy, and reminder email timing. The bandit algorithm learns which combinations lead to the most completed applications and automatically prioritizes those paths.
Outcome: The brand reduces friction in the onboarding flow and identifies the highest-converting form and message combination, increasing successful sign-ups.
Industry: Subscription and DTC (direct-to-consumer) brands
Goal: Find the most effective retention offer for at-risk subscribers.
Example use case: The marketing team tests several personalized offers—discounts, loyalty points, or free upgrades—delivered via email and in-app messages. The multi-armed bandit algorithm monitors response rates and optimizes distribution toward the incentives that drive the highest reactivations.
Outcome: The brand identifies the strongest retention strategy for each customer segment, reducing churn and increasing lifetime value.
Real-world applications: personalization, messaging, and offer testing
The principles behind multi-armed bandit testing come to life in how brands personalize campaigns at scale. A strong example comes from Kayo Sports, Australia’s leading sports streaming platform, which uses adaptive decisioning to keep millions of fans engaged.
While standard multi-armed bandits optimize based on performance data alone, contextual bandits take the idea further by factoring in the context surrounding each user interaction. This includes attributes such as location, device, or past engagement. The algorithm learns which one performs best for each customer in a given moment. This added layer of intelligence makes contextual bandits a cornerstone of adaptive, AI-driven personalization.
Kayo Sports keeps fans engaged with adaptive messaging
Kayo Sports gives viewers access to more than 50 live and on-demand sports, delivering high-energy experiences that match the pace of live events.
The challenge
With multiple leagues, time zones, and constantly changing schedules, Kayo needed to reach each user with timely, relevant updates—something manual segmentation and static campaigns couldn’t achieve.

The strategy
Using Braze, Kayo applied adaptive decisioning that mirrors multi-armed bandit logic. The system analyzed live viewing and engagement data, then selected the best message, offer, or reminder for each user in real time. Every send acted as a learning signal, helping the system continually refine message selection and timing as events unfolded.
The results
- 2.5x increase in conversion rates across triggered campaigns
- 20% lift in message engagement
- Significant reduction in churn through personalized retention journeys
By applying multi-armed bandit principles to its engagement strategy, Kayo built a marketing approach that learns as fast as its fans do—responsive, data-driven, and always in motion.
How Braze uses intelligent selection to bring MAB to life
The Braze AI Decisioning Studio™ incorporates multi-armed bandit (MAB) logic and intelligent selection as part of its optimization framework, helping marketers automate decisions that once relied on static rules or manual testing.
Within this system, MAB algorithms handle the allocation problem—deciding how much traffic or exposure to assign to each message or offer while the campaign is live. They do this by combining exploration (testing new options) with exploitation (serving proven winners) using live engagement data.
This functionality works alongside other decisioning models within the suite, such as contextual bandits for real-time personalization and predictive scoring for next-best-action decisions.
The MAB framework in Braze leverages reward-based reinforcement learning. Each campaign interaction feeds back a “reward” signal (for example, a click or purchase), allowing the model to continually update its confidence levels across all variations. That feedback process is what enables the system to adapt within seconds rather than hours or days.
By embedding multi-armed bandit optimization within a larger AI decisioning architecture, Braze gives marketers access to adaptive experimentation at scale—combining statistical efficiency with the flexibility needed for fast-moving campaigns.
Key takeaways: smarter experiments, faster wins
Multi-armed bandit testing gives marketers a faster, more adaptive way to optimize campaigns. It builds learning directly into campaign delivery—continuously improving as engagement data flows in.
Key points to remember:
- Real-time learning: Each interaction feeds back into the system, allowing campaigns to adjust instantly.
- Efficiency at scale: Traffic automatically shifts toward high-performing messages or offers, helping to reduce wasted impressions.
- Dynamic optimization: Testing and execution happen together, creating a self-improving process that keeps performance aligned with audience behavior.
- Wider application: The same logic can guide decisions around timing, channel selection, or creative direction—not just message testing.
- Strategic balance: Use A/B testing for foundational direction and multi-armed bandits for ongoing fine-tuning and real-time personalization.
Discover how the Braze AI Decisioning Studio™ uses multi-armed bandit optimization to make every message smarter and more impactful.
FAQs about the multi-armed bandit
What is a multi-armed bandit algorithm in marketing?
A multi-armed bandit algorithm in marketing is a type of machine learning model that automatically tests and reallocates campaign traffic toward the best-performing variation as results come in. It allows marketers to optimize messaging, offers, or timing in real time rather than waiting for a traditional test to end.
How does multi-armed bandit testing differ from A/B testing?
Multi-armed bandit testing differs from A/B testing because it learns while the campaign runs. A/B testing splits audiences evenly and waits for statistical proof before a winner is chosen. Bandit testing continuously shifts traffic toward higher-performing options, helping campaigns reach better results faster.
Why is the multi-armed bandit approach better for personalization?
Because it adapts as behavior changes, the multi-armed bandit approach is ideal for personalization. It continually identifies which messages or offers resonate most with each segment, improving relevance and engagement over time.
How can marketers apply bandit testing in campaign optimization?
Marketers can apply bandit testing to creative variations, channel selection, offers, or send times. The algorithm monitors live engagement data and automatically directs more impressions to the options that work best for each audience.
How is multi-armed bandit testing used in real-time marketing experiments?
In real-time marketing, multi-armed bandit testing helps campaigns evolve as data flows in. Each interaction becomes a signal that influences the next decision, allowing optimization to happen continuously.
How can AI decisioning and multi-armed bandits work together?
AI decisioning platforms often include multi-armed bandit models as part of their optimization engine. The algorithm handles dynamic allocation, while the AI layer uses contextual and predictive data to decide which message, channel, or action is most effective for each user.
What is the difference between A/B testing and bandit testing in marketing?
A/B testing focuses on controlled comparisons and clear statistical validation. Bandit testing focuses on learning speed and performance gains during live campaigns. The two methods complement each other—A/B testing sets direction, while multi-armed bandit testing keeps optimization running in real time.
Related Tags
Be Absolutely Engaging.™
Sign up for regular updates from Braze.
Related Content
 Article5 min read
Article5 min readRamadan revelations: Mastering customer engagement in the GCC with AI
March 06, 2026 Article4 min read
Article4 min readBuilding spaces for connection: Inside our Bucharest office
March 05, 2026 Article7 min read
Article7 min readData agility at a massive scale: How the Braze Data Platform supports customer engagement
March 04, 2026