AI decision making: How brands use intelligent automation to scale personalization and drive revenue
Published on January 30, 2026/Last edited on January 30, 2026/10 min read

Team Braze
Contents
- Why AI decision making matters now
- What is AI decision making?
- How AI decision making works: AI decisioning and AI agents
- AI decision making vs. traditional marketing approaches
- How AI decision making personalizes marketing and lifecycle journeys
- How AI decision making differs from AI hype
- Key challenges and how to overcome them
- How to choose an AI decisioning platform
- Future trends in AI decision making
- Key takeaways on AI decision making
- FAQs about AI decision making
Many teams already use data and automation across their customer journeys. What’s changing now is how decisions get made in real time. AI decision making focuses on those decisions themselves and turns them into something you can manage, measure, and improve at scale.
Using techniques like machine learning optimization and reinforcement learning (RL), brands can move from isolated tactics to a shared decision layer that supports marketing, operations, customer service, and strategy. The same system that selects a message or offer for an individual can also help protect margin, reduce churn, and support better use of resources.
This guide looks at how AI decision making works, what makes it different from traditional approaches to AI, and how engagement teams can use it as a practical, cross-functional tool rather than a theoretical concept.
Why AI decision making matters now
AI decision making matters now because customer expectations and business pressures are rising at the same time –and static rules can’t keep up. People want relevant, low-friction experiences across channels, while teams face tighter budgets, stricter privacy rules, and journeys that are too complex to manage with static segments and fixed calendars.
By using intelligent automation and updating decisions based on live behavior and outcomes, AI decision making helps brands have a shared way to connect individual experiences with wider goals around growth, efficiency, and satisfaction.
What is AI decision making?
AI decision making uses machine learning to make decisions for customers and prospects at the 1:1 level, broken down into AI decision making and AI agents.
How AI decision making works: AI decisioning and AI agents
AI decision making uses machine learning to make decisions for customers and prospects at the 1:1 level. Two building blocks do most of the work: AI decisioning, which learns what to do next for each person, and AI agents, which help apply those decisions across journeys and conversations in a more human way.
Predictive models and scores can feed into this, but they are inputs. AI decisioning is where “next best everything” happens — choosing the right treatment, channel, timing, and whether to contact someone at all.

AI decisioning for 1:1 personalization
AI decisioning starts with three elements:
- An action bank: the eligible messages, offers, channels, timings, or a choice to send nothing
- A goal: such as activation, renewal, revenue, or long-term value
- A feedback signal: what happened after each decision, for example a view, click, purchase, or churn
Reinforcement learning uses this setup to learn from experience. The system tries different actions for different people, sees the outcomes, and treats those outcomes as signals against the goal

Over time, it becomes better at choosing which action from the bank is likely to help a given customer take a valuable next step. Contextual bandits are one family of these methods, used for fast, single-step choices — for example, which subject line or creative to show, which promotion card to use, or whether to send anything in that moment.
A key point to remember is that predictive analytics might say who is likely to convert or churn, but AI decisioning is what turns that insight into decisions — picking the specific treatment, channel, and timing for each person. That’s how BrazeAI Decisioning Studio supports “next best everything,” not just next-best-offer.
This is decision automation built on machine learning optimization, continuous experimentation, and genuinely data-driven decisions, rather than static rules or one-off A/B tests.
Autonomous agents for more human, context-aware response
AI agents are autonomous systems that deliver more human, context-aware experiences across the lifecycle. They can decide how to respond and how that response shows up for the customer.
Marketers set the goals, guardrails, and action banks agents can work with. Predictive AI, scores, or segments can inform those decisions, but AI decisioning remains the engine that chooses next steps, and AI agents are how those choices turn into more natural conversations and flows.
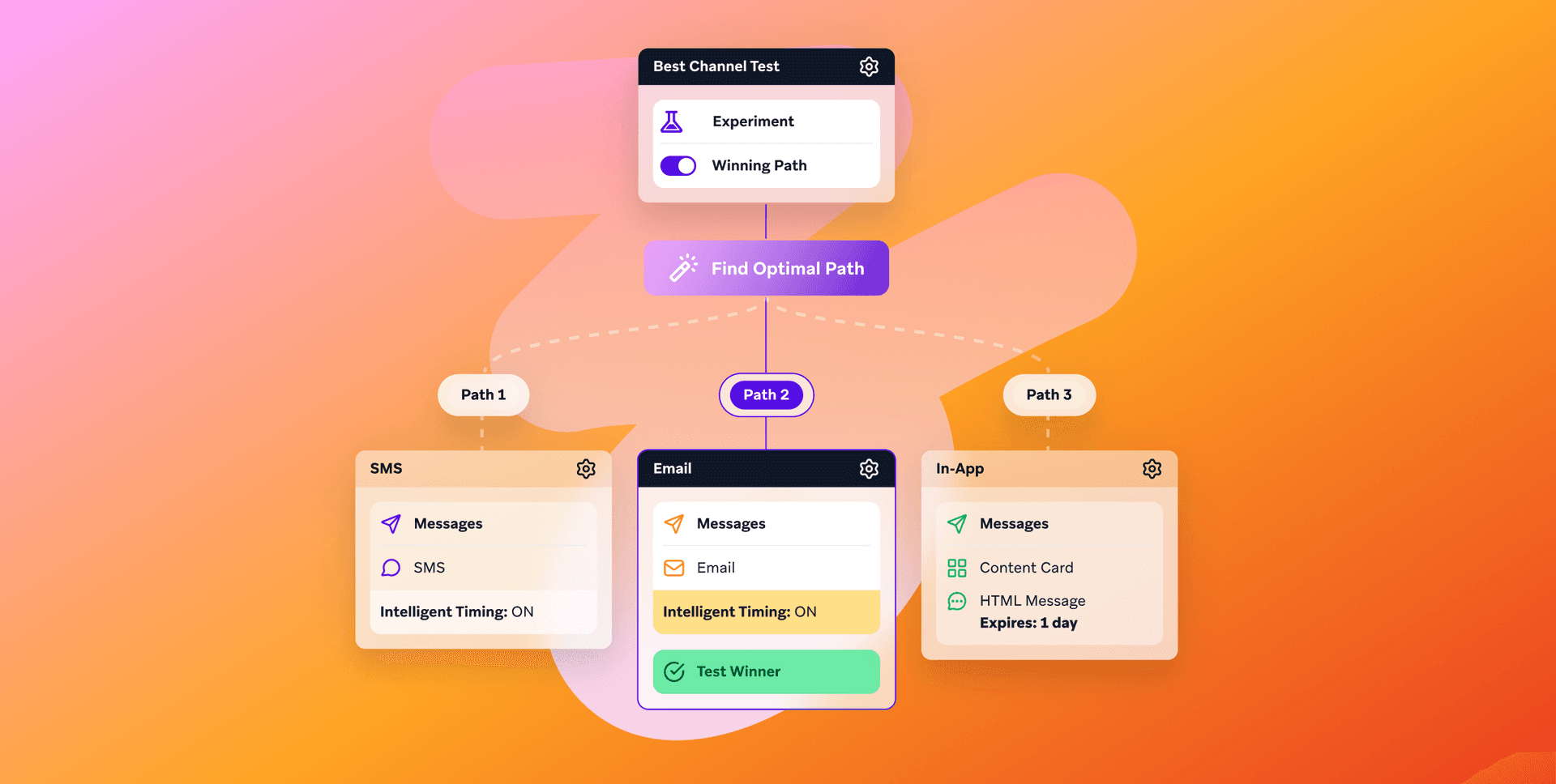
AI decision making vs. traditional marketing approaches
Traditional marketing often personalizes at the segment level and builds decisions into fixed rules and calendars. AI decisioning shifts that to the individual, updating who to contact, what to send, and when based on each person’s behavior and context. Instead of relying on static rules or one-time predictive scores, AI decision making keeps learning from outcomes and adjusts those individual decisions automatically, so journeys stay relevant without constant manual redesign.
The table below highlights some of the main differences.
Area | Traditional marketing decision-making | AI decision making |
|---|---|---|
How decisions are managed | Rules and journeys are set upfront and revisited periodically | Decision policies can adjust over time based on how people actually respond |
Personalization scope | People in the same segment follow roughly the same path | Designed to tune choices to the individual customer’s current context and history |
Experimentation style | Planned A/B tests with a few variants and fixed end dates | Testing runs continuously, with traffic moving toward options that perform better |
Timing and frequency | Fixed calendars and simple triggers (for example, “send after X days”) | Contact cadence adapts to engagement and fatigue signals, including when to hold back |
Channels | Each channel has its own plan and KPIs | Decisions are made from a shared view of the customer across channels |
Role of data | Mainly used for reporting and occasional targeting tweaks | Feeds directly into the decision layer so future actions are influenced by observed outcomes |
How AI decision making personalizes marketing and lifecycle journeys
There are many ways AI decision making can personalize a customer journey. At each step, it helps decide how to motivate each person toward a more valuable outcome. Here are some real-life examples of how teams use it to drive the next step.
AI decisioning can be used to:
- Improve trial and onboarding by trying different mixes of education, prompts, and offers, then steering each new customer toward the sequence that actually helps them get value fastest.
- Grow upgrades and add-ons by timing higher-tier offers or cross-sell prompts around real product usage, rather than following a fixed schedule.
- Reduce churn and revive dormant users by adjusting outreach style, cadence, and incentives according to risk level and how they’ve responded in the past.
Underneath, AI decisioning is choosing between messages, offers, wait times, and pauses for each person based on your goals and live feedback, instead of running one standard journey for everyone.
AI agents carry these decisions into more conversational, human-feeling touchpoints. They can use the same signals to:
- Suggest a tailored WhatsApp or SMS reply
- Trigger a specific Canvas path after a support chat
- Shift follow-up messaging for someone who’s just had a great or poor experience
AI decisioning focuses on which option is most likely to move someone toward a better outcome at the 1:1 level; AI agents help shape how that choice is expressed to the customer.
How AI decision making differs from AI hype
AI decision making is about running real decisions in production, with clear objectives, continuous testing, and automation teams can understand and control. AI decisioning uses a shared decision layer across journeys and channels, with humans setting goals, guardrails, and brand standards, and defining governance and privacy strategies from the start.
Hype focuses on features; AI decision making is judged on whether it reliably moves customer and business metrics in the right direction.
Key challenges and how to overcome them
Adopting AI decision making often raises concerns over loss of control, data readiness, and how much change the team can handle. A few grounded moves can make it feel more manageable.
“Will this replace my team?”
AI decision making is decision support and automation, not a substitute for marketers or product owners. Keep humans in charge of priorities, guardrails, and brand standards, and use decisioning to handle high-volume choices like who to contact, when, and how often.
“Our data isn’t perfect.”
You don’t need a flawless dataset to start. Begin with one or two journeys where you already have solid first-party data and clear goals, then expand signals and use cases as you see consistent lift and learn from what’s working.
“How do we trust the system?”
Treat trust as a design requirement. Define which actions are allowed, choose simple reward signals tied to real outcomes, use control groups, and review policies regularly so teams can see how decisions are being made and step in when needed.
“This feels like a big change.”
Frame decisioning as a shift in focus, not a full rebuild. Start with a pilot use case, give a cross-functional group clear ownership, and use what you learn to guide wider rollout (rather than trying to switch everything over at once).
How to choose an AI decisioning platform
Braze approaches AI decision making through the lens of customer engagement, with decisioning built into the same platform that runs journeys, messages, and campaigns in real time.
For teams, a few things stand out:
- Native to engagement, not just reporting: BrazeAI Decisioning Studio™ sits between your first-party data and channels like email, push, SMS, and in-app, so decisions about message, timing, and frequency can be applied directly in live journeys rather than exported as recommendations.
- Reinforcement learning and bandits built in: Decisioning uses reinforcement learning and contextual bandits to keep testing within an action bank and update policies based on how customers respond, helping replace manual A/B tests with continuous optimization.
- 1:1 decisions across key levers: The system can tailor multiple dimensions at once—channel, creative, offer, and cadence—at an individual level, making large-scale personalization more practical for brands with complex products and audiences.
- Open data and marketer control: Braze connects to existing warehouses and CDPs, uses those signals in decisioning, and gives marketers control over KPIs, guardrails, and action banks, with visibility into how policies are performing over time.
When you choose an AI decisioning platform, the technology is only part of the story. You also need people who can connect your data stack, keep signals clean, and make experimentation part of day-to-day work. At Braze, forward-deployed data scientists act as a bridge between a brand’s warehouse, events, and BrazeAI Decisioning Studio™.
They are there to support your use in tasks such as connecting customer data with our system so that our AI agents can take the data, learn from it, and send the right information back to these businesses. They also help brands define success metrics, set up decisioning for specific use cases, and read the impact on KPIs like revenue, retention, and engagement.
These capabilities give brands a way to apply AI decision making directly to the experiences customers receive, while still fitting into modern data stacks and keeping marketers in charge of how automation is used.
Future trends in AI decision making
AI decision making is likely to shift from a specialist capability to part of the fabric of how brands run engagement and operations. The focus will move from “where can we test this?” to “which decisions should this handle by default?”
Over time, you can expect more agent-based systems looking after areas like onboarding, monetization, and churn, with teams defining objectives and action banks rather than individual rules. Decisioning will sit behind conversations as well as campaigns, drawing on richer real-time signals from product, payments, and support.
Leaders will put more emphasis on responsible AI and multi-objective optimization, asking decisioning to balance growth, margin, and customer experience while meeting higher standards for consent, auditability, and fairness.
Key takeaways on AI decision making
AI decision making is less about adding new channels and more about changing how choices get made across the ones you already use. These points can help you explain it to stakeholders and decide where to start.
- AI decision making focuses on what happens next for each person, learning from outcomes and applying those learnings at an individual level.
- Humans define goals, guardrails, and brand standards; decisioning turns that direction into day-to-day execution at scale.
- You can start with a few high-impact journeys and existing data, then expand signals and use cases as you see lift.
- Continuous experimentation becomes part of the way you work, so offers, content, and cadence keep improving without constant manual test setup.
With Braze, AI decision making sits inside your engagement platform, shaping live cross-channel experiences instead of living only in reports or planning tools.
FAQs about AI decision making
What is AI decision making, and how does it differ from traditional AI?
AI decision making uses AI decisioning to choose which option to serve each customer at the 1:1 level, based on goals, an action bank, and live feedback. Traditional AI, including rule-based systems and traditional predictive AI models, usually stops at scores or classifications, while AI decision making turns those and other signals into live, adaptive decisions.
How does reinforcement learning power AI decision making?
Reinforcement learning lets an agent try actions, see the results, and treat those results as signals against a goal like revenue, retention, or activation. Over time, that learning helps AI decisioning pick treatments—such as messages, offers, or timings—that are more likely to drive better outcomes for each person.
What are real-world examples of AI decision making in marketing?
Real-world examples of AI decision making in marketing include choosing offers in winback journeys, adapting onboarding flows by behavior, and optimizing creative or send times with bandit-style testing. In each case, AI decision making helps tailor actions to individuals instead of relying on one fixed journey.
What’s the difference between AI decision making and predictive AI?
Traditional predictive AI highlights who is likely to behave a certain way, for example by scoring churn or conversion risk. AI decision making uses those signals, plus live context, to decide how to respond by automating channel, content, and timing choices for each person.
How can AI decision making improve customer engagement and ROI?
AI decision making improves customer engagement and ROI by matching each person with messages, offers, and cadence that are more likely to drive meaningful outcomes. Because testing runs continuously, the system can lift conversion and retention while reducing wasted impressions and blanket discounts.
What data is needed for effective AI decision making?
Effective AI decision making starts with solid first-party data, such as events, core attributes, and lifecycle milestones. Brands can then add richer signals like product usage, service interactions, and sentiment to give decisions more context and more context for 1:1 choices.
How can mid-market brands adopt AI decision making without specialists?
Mid-market brands can adopt AI decision making by using platforms with built-in AI decisioning and AI agents that marketers can configure. Starting with a few clear use cases—such as a trial flow or a churn-risk journey—and using visual tools for goals, action banks, and guardrails helps teams prove value without dedicated ML roles.
What are contextual bandits and why do they matter for AI decisions?
Contextual bandits are a type of reinforcement learning model that choose one action for a specific situation, learn from the immediate response, and reuse that learning in similar contexts. They matter because they support fast, 1:1 experimentation on choices like subject lines, creative, or offers without long, manual test cycles.
How does AI decision making help brands scale personalization?
AI decision making helps brands scale personalization by using decision policies that choose offers, content, channels, and timing for each individual instead of relying on static rules. This lets teams run 1:1 experiences across large audiences without managing every decision by hand.
Related Tags
Be Absolutely Engaging.™
Sign up for regular updates from Braze.
Related Content
 Article12 min read
Article12 min readLeaders in marketing: Celebrating the women redefining customer engagement on International Women’s Day
March 09, 2026 Article4 min read
Article4 min readClosing the retail experience divide
March 09, 2026 Article5 min read
Article5 min readRamadan revelations: Mastering customer engagement in MENAT with AI
March 06, 2026